This type of joint is like two bowls nested together. Joints can be classified by the type of the tissue present fibrous cartilaginous or synovial or by the degree of movement permitted synarthrosis amphiarthrosis or diarthrosis.
Describe the structures that support and prevent excess movements at each joint.
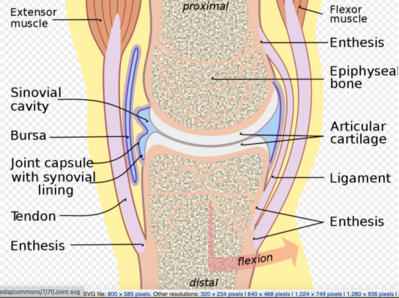
. This joint capsule constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity and surrounds the bones articulating surfaces. Diarthrosis joints are the most flexible type of joint between bones because the bones are not physically connected and can move more freely in relation to each other. Synovial joint at which the rounded portion of a bone rotates within a ring formed by a ligament and an articulating bone.
The synovial cavityjoint is filled with synovial fluid. A synovial joint is characterised by the presence of a fluid-filled joint cavity contained within a fibrous capsule. A synovial joint is a connection between two bones consisting of a cartilage lined cavity filled with fluid which is known as a diarthrosis joint.
Hinge Ball-and-socket - Multiaxial joint hinge - Monaxial joint moving freely in one plane with very little movement in any other. Synovial cavities are filled with synovial fluid. Functionally classified as a multiaxial joint proximal radioulnar joint.
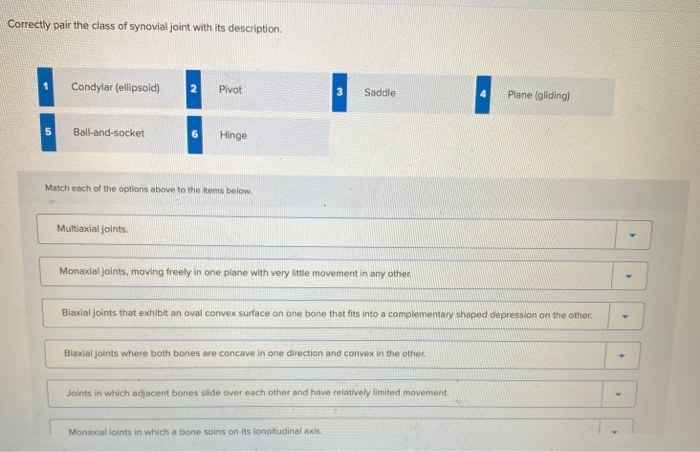
Describe the bones that articulate together to form selected synovial joints. Correctly pair the class of synovial joint with its description. Only multiaxial joints in the body where one bone fits into a cuplike socket of the other shoulder and hip joints 2.
Bone cartilage synovium synovial fluid and tensile tissues composed of tendons and ligaments. Multiaxial joints Monaxial joints moving freely in one plane. Biaxial joints that exhibit an oval convex surface on one bone that fits into a complementary shaped depression on the other.
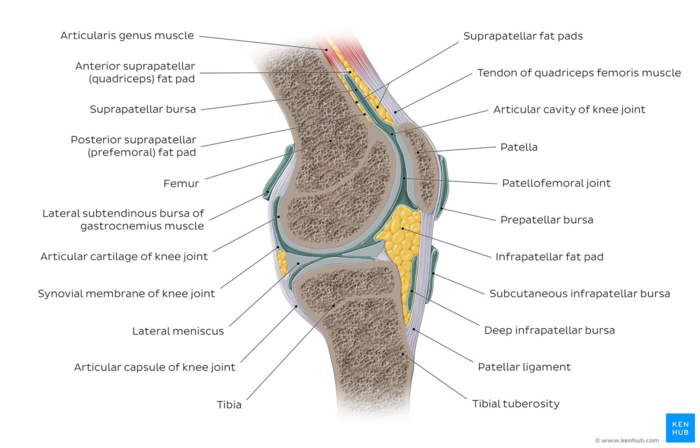
The knees and elbows are examples of synovial joints. Plane joint slide against each other as multiple movements. It is the most common type of joint found in the human body and contains several structures which are not seen in fibrous or cartilaginous joints.
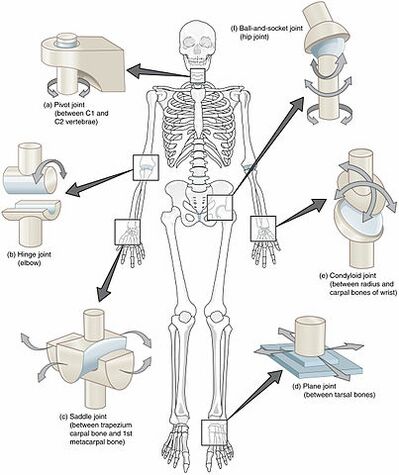
Multiaxial joints Monaxial joints moving freely in one plane with very little movement in any other. The different types of synovial joints are the ball-and-socket joint shoulder joint hinge joint knee pivot joint atlantoaxial joint between C1 and C2 vertebrae of the neck condyloid joint radiocarpal joint of the wrist saddle joint first carpometacarpal joint between the trapezium carpal bone and the first metacarpal bone at the base of the thumb and plane joint facet. Correctly pair the class of synovial joint with its description Condylar ellipsoid Pivot Saddle Plane gliding Ball-and-socket Hinge Match each of the options above to the items below.
In this article we shall look at the classification of joints in the human. Each synovial joint of the body is specialized to perform certain movements. Which of the following correctly pairs the synovial joint and the general movement associated with it.
The synovial joints are classified according to the shapes of the articulating surfaces and the types of movements and range of motion they permit see Figure 334. Correctly pair the class of synovial joint with its description Condylar ellipsoid Pivot Saddle Plane gliding Ball-and-socket Hinge Match each of the options above to the items below. The different subtypes of joints are balland socket hinge pivot ellipsoidal or condyloid saddle and gliding or planar.
These joints may alsobe classified as nonaxial monaxial. A synovial joint sometimes called diarthrosis joins bones with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity and surrounds the bones articulating surfaces the most movable type of joint in the body. Correctly pair the class of synovial joint with its description.
These joints can be described as planar hinge pivot condyloid saddle or ball-and-socket joints. Hinge joints are the synovial joint type referred to in our introductory section. Anatomy and Physiology questions and answers.
Synovial joints are made up of five classes of tissues. Discuss the movements available at each joint. The synovial lining in the bursae and tendon sheaths similar to that within joints is a slippery non-adherent surface allowing movement between planes of tissue.
Oval convex surface on one bone fits into a complementary shaped depression on. A synovial joint connects bones with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the bones periosteum. Functionally classified as uniaxial joint plane joint synovial joint formed between the flattened articulating surfaces of adjacent bones.
The shape of the joint affects the type of movement permitted by the joint Figure 1. Multiaxial joint- Ball and socket Monaxial moving freely in one plane with very little movement in any other-Hinge. You are allowed to ignore this though as you only need to know about the synovial joints which.
A synovial joint also known as diarthrosis joins bones or cartilage with a fibrous joint capsule that is continuous with the periosteum of the joined bones constitutes the outer boundary of a synovial cavity and surrounds the bones articulating surfaces. Correctly pair the class of synovial joint with its description. Your hip and shoulder joints are the only ball-and-socket synovial joints in your body and you use them whenever you hug walk or high-five.
Condyloid Joints Condyloid joints have an irregular surface where the bones move past one another. Synovial joints are further classified into six different categories on the basis of the shape and structure of the joint. Ball-and-socket anterior-posterior plus medial-lateral directions hinge joint straightening motions along a single axis All options are correct.
This joint unites long bones and permits free bone movement and greater mobility. Biaxial joints where both bones are concave in one direction and convex in the other Joints in which adjacent bones slide over each other and have relatively limited movement. The structure and function of synovial joints is our second dash point under the skeletal system.
These joints can be found between your upper and lower arm bones otherwise called your elbow as well as your. The movements that are allowed are determined by the structural. The skeletal system has a number of different joint types for example there are fibrous joints and there are cartilaginous joints.

Solved Correctly Pair The Class Of Synovial Joint With Its Chegg Com
0 Comments